Researchers Find Cannabinoids Applied To The Eye, Widen Field of Vision
Researchers from the Montreal Neurological Institute say using marijuana may help your night vision by decreasing the eyes’ sensitivity to light.
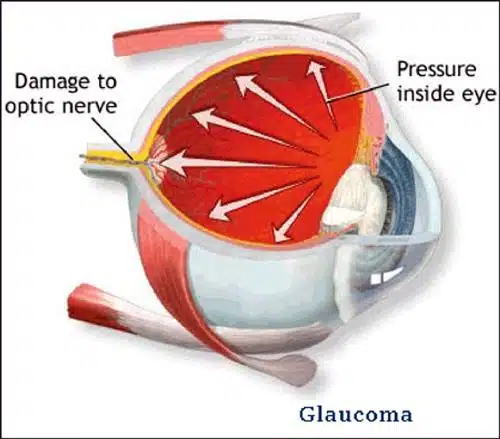
One side effect of marijuana use on the eye, is redness. THC, a naturally occurring cannabinoid, lowers blood pressure, which dilates the blood vessels. The increase in blood flow to the body, causes the blood vessels in the eye to expand and causes redness. This is the same reaction that makes marijuana an effective Glaucoma treatment. The researchers from the study discovered applying a lab made cannabinoid directly to eye tissue made the cells more sensitive by increasing the rate they reacted to bright and dim light stimuli.
Findings of the Study
“Initially you distrust yourself when you see something that goes against widely held ideas, but we tried the experiment so many times, using diverse techniques, and it was a consistent result,”-Ed Ruthazer, senior author of the paper, A professor of neurology and neurosurgery at the Montreal Neurological Institute of McGill University, in a statement.
In the study, the researchers applied synthetic cannabinoids to the eye tissue of tadpoles. The researchers chose African clawed toad for one group, while the other group acted as a control. Researchers chose to observe tadpoles because like humans, their eyes also contain CB1 protein, a receptor in the endocannabiniod system, which binds the psychoactive ingredient of marijuana (THC). The tadpoles were in a petri dish, researchers placed black marks on the outside shaped to look like predators shadows.

Results
“Taken together, these data suggest a model in which activation of CB1Rs on RGCs should enhance their excitability enough to recruit RGCs to fire action potentials in response to visual stimulation of subfields that were previously sub-threshold. This should manifest as an enlargement of input receptive field (RF) sizes in tectal neurons, which receive convergent inputs from many RGCs.”
The results of the study showed that the Cannabinoids applied to the eye, caused the toads to see in an area that had previously been sub-threshold. Cannabinoids widened the field of vision.
Source: Miraucourt LS, Tsui J, Gobert D et al. Endocannabinoid signaling enhances visual responses through modulation of intracellular chloride levels in retinal ganglion cells. eLife. 2016.